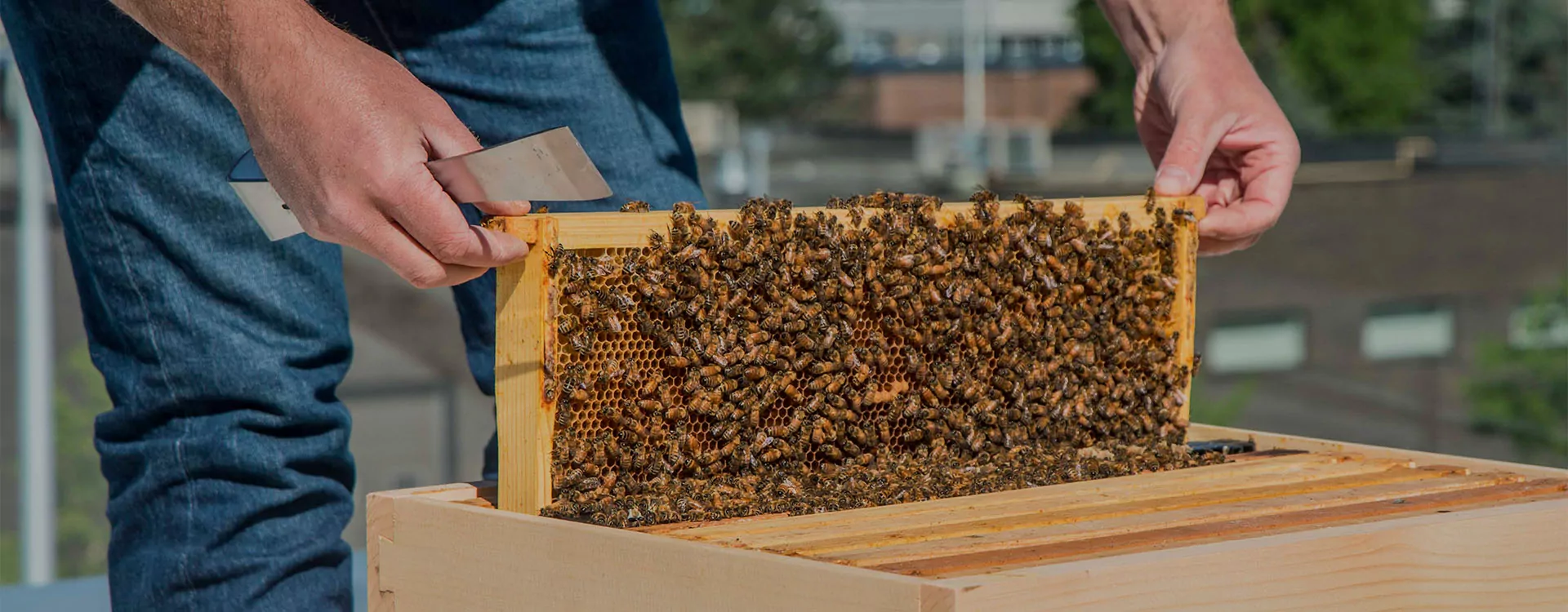

Beekeeping Equipments
Bees are managed in modern hives. The hive design is based on the principle of “bee space”. There is space between the frames, between top bars of frames and inner cover and between the frames and inner walls and this space allows the free movement of bees. Because of the bee space the parts are not attached to each other. Hive is composed of bottom board, brood chamber, brood chamber frames, super chamber and super frames, inner cover and top cover. There are different types of hives, with different bee spaces, being used for different species and races of bees.
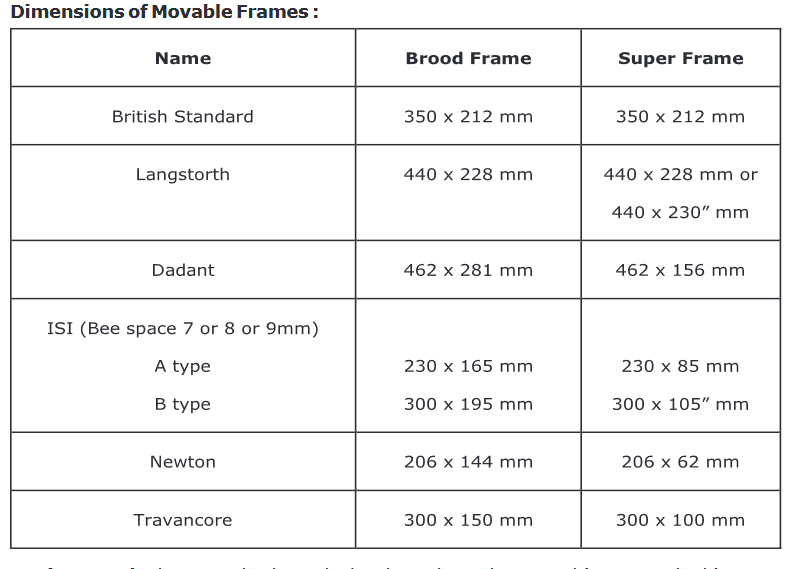
BEE HIVES
Bee hives were designed after the discovery of "Bee Space" (or) "Bee Passage" by L. L.
Langstroth. It is the optimum distance to be left in between two adjacent comb surfaces in a bee hive which is essential for normal movement and functioning of bees. It is too small for
comb construction and is too large for propolis deposition. It varies with honey bee species.
e.g. Indian bees - 7 - 9 mm: Italian bees - 10 mm.
- Hive volume can be increased (or) decreased based on need.
- Bees can be fed artificially.
- Artificial queen rearing can be done.
- They allow easy inspection and manipulation of colonies.
- They allow very efficient honey harvesting because the honeycombs, within their frames, can be emptied of honey and then returned to the hive.
Advantages of bee keeping in movable frames
Types
The British standard hive, Jeolikote villager hive, I.S.I hive: “A Type” I.S.I hive: “B Type” Newton's hives, BIS hives and Marthandam hives are suited for rearing Indian bees. Langstroth hives are suited for rearing Italian bees.
A. Langstroth ten- frame hive
1) Stand: Four legged stand 15-25 cm high to support the bottom board properly.
2) Bottom board: it can be made either by taking a piece of wood 550mm long, 450 mm broad and 22 mm thick, or by joining 2 wooden boards together nailing in position with wooden rods. Along each end of the longer side is nailed a wooden rod 550 mm long, 22 mm broad and 22 mm thick and another wooden rod 363 mm x 22mm is nailed at the back. The front is provided with entrance rod which is 363 mm x 22 mm x 22 mm and this has an entrance 75 mm long and 22 mm deep in its middle.
3) Brood chamber: It is a rectangular box without top and bottom and is made of 22
mm thick wood. Its length on the outside is 406 mm and on the inside 363 mm
and its height is 238 mm. A rabbet 16 mm deep and 13 mm wide is cut along the
entire of its width planks.
4) Frame consist of top bar, two side bars and a bottom bar dimensions for self spacing frame are given below
(i) Top bar: 475 mm long, 25 mm wide and 22 mm thick. It is cut to 9 mm
thickness on both sides for a length of 25 mm. it has a groove, in the
middle of its lower side for fixing the comb foundation sheet.
(ii) Side bar: each is made up of 9 mm thick wood and is 226 mm long. The upper part of each is 34 mm wide and lower part 25 mm wide. Each is cut from the middle portion at either end to accommodate the top and the
bottom bars, respectively. There are 4 holes in each side bar for wiring the frame.
(iii) Bottom bar: 440 mm long, 19 mm wide and 9 mm thick. The outside measurements of the frame are 440 mm x 228 mm.Two 15 mm staples should be driven in (to leave only 9 mm outside) to top bar on its opposite side, so that the frames stand 34 mm apart. Tinned wire of 28 gauge should be used in wiring the frame.
5) Super:The dimensions of the super and the super frames should be same as those of the brood chamber and brood chamber frames, respectively.
6) Inner cover: This is a wooden board to cover the brood chamber or the super as th case may be. It is 500 mm long, 406 mm broad and 9 mm length wood. It has 9 mm thick and 22 mm wide wooden bar nailed on to each of its four sides.
7) Top cover: It is made up of 9 mm thick wooden board nailed to a rectangular frame 50 mm high ,all covered over with a metallic sheet so as to make it impervious to rain water. Its inside measurements are 525mm x 425 mm. It rests loosely over the hive.
This is used to keep the bee hive above the ground (15-25 cm high) so as to protect the colony from termites, ants and other crawling insects, as also prevent soil moisture getting into the hive or facilitate ventilation from below the hive.
This is a machine to prepare comb foundation sheet used in beekeeping to make bees build regular combs in frames, that are convenient to handle.
: It is a thin sheet of bee wax embossed with a pattern of hexagons of size equal to the base of the natural brood cells on both sides. For A. mellifera there are 19 cells and for A.cerana 22- 23 cells/100 mm linear length.
A spur embedder or an electric embedder and transformer is used to embed wires into the comb foundation sheets
A wooden board of the size of a frame placed inside the brood chamber, used to reduce the size of the bee nest in a hive. Dummy board is used to reduce the free space in the hive that helps the bees in containing heat within the nest and also useful to protect them from enemies.
Used for providing sugar syrup as feed to the bees during dearth period.
It is a cage made up of wood or wire gauge or plastic structure used for queen introduction of transport of queen either with a few attendant worker bees, in packages
Piece of queen excluder sheet with holes large enough to allow free movement of worker bees, but too small to allow queen's passage. Queen gate is used to arrest the queen bee in the hive, during seasons of food scarcity or during inclement weather, when there is a danger of bees deserting the hive.
A flat metal screen with parallel slots of 4.0 to 4.2 mm width is placed above the brood chamber to prevent queen going into the honey storage area above, and laying eggs in the honey combs.
It is a cone shaped structure made of a piece of wire wound spirally used to protect the queen cell, given from a queen right to queen less colony until its acceptance by bees.
This is a wooden or metal device which allows the bees to go through a self closing exit.
This is a device attached to the bee hive to remove pollen loads from the returning pollen foragers and to collect them in a tray.
This device is used at the entrance to reduce the drone population inside the hive.
It is a rectangular box used to trap and carry the swarm. It is fixed near the hive entrance with one or two combs inside during the swarming season.
This is a flat metal rod of varying design and size used commonly while handling bees in the hive.
A beekeeper uses a smoker to produce cool smoke to calm the bees while handling them.
a. Bee Veil: It is worn over the face for protection against stings.
b. Gloves: These are used while inspecting and handling colonies to protect hands and
arms.
c. Overalls: Light coloured cotton materials are preferable since they are cooler and create
less risk for antagonizing bees.
d. Boots: A pair of gum boots will protect the ankles and prevent bees from climbing up
under trousers.
This is used to hold a swarm of bees and transport it to the apiary.
A soft camel-hair brush is used to remove bees off the honey comb before it is taken out for extraction of honey.
Single or double edged steel knife is used for removing wax cappings from the honey comb before putting it in the honey extractor.
Helpful tool for holding frames when inspecting the colony.
This is a metal drum or barrel with a gear mechanism to rotate a honey frame holder kept in it. Honey combs are kept in the extractor after removing the caps on the cells. After removal of honey, the combs can be re-used in the hive since the cells and the comb remain intact.